最终401例患者入围该研究�
。随访时间中位数是48天(包含23天到129天)��
。患者的分类信息及临床特征如表格1所示��
。
表格 1患者统计和临床特征
Factors | Total population of the study(n=401) |
Age(range) | 61.8±15.5(18-91) |
Male/female, no. of patients | 228/173 |
Body weight (range) | 51.7±10.5(28.6-110.6) |
Primary disease, no. of patients(rate) |
|
Haematological malignancy | 157(39.2%) |
Collagen disease | 88(21.9%) |
Solid organ malignancy | 39(9.79%) |
Benign respiratory tract disease | 23(5.7%) |
Diabetes | 17(4.2%) |
Inflammatory bowel disease | 17(4.2%) |
Skin and soft tissue disease | 12(3.0%) |
Solid organ transplantation | 4(1.0%) |
Liver cirrhosis | 13(3.2%) (Child-Pugh A, 2;B,4;C,7) |
Chronic renal disease | 7(1.7%) |
Neurological disease | 6(1.5%) |
Other | 31(7.7%) |
Diagnosis of the fungal disease, no. of patients(rate) |
|
Proven | 99(24.79%) |
Candidiasis | 46 |
Aspergillosis | 37(coinfection with cryptococcosis:1) |
Cryptococcosis | 9 |
Other | 8 |
Probable/possible | 209(52.19%) |
Undiagnosed (empirical therapy) | 93(23.2%) |
Route of administration in initial therapy |
|
Intravenous | 119(29.7%) |
Oral | 282(70.3%) |
在接受负荷剂量的患者中��
,初始治疗日的中位剂量(IQR)为5.9 mg/kg��
,每日2次(5.4 ~ 6.1)��。维持剂量中位值为3.8 mg/kg��。TDM的实施主要在治疗开始后6天左右��
。血药谷浓度中位值为3.33 ug/ml��
。其中��
,29.6%的患者Cmin≥5 ug/ml��
,6.6%的患者≤1 ug/ml(如表格2所示)��
。
表格 2 伏立康唑初始谷浓度
Initial Cain | Total(n=401) | Adequate dosing and timing of TDM(n=226) |
| (interquartile range) (ug/mL) | 3.33(1.90-5.13) | 3.91(2.50-5.48) |
Cmin categories |
|
|
<1ug/mL | 44(11.0%) | 15(6.6%) |
1-5ug/mL (target concentration range) | 249(62.19%) | 144(63.79%) |
≥5ug/mL | 108(26.9%) | 67(29.69%) |
治疗过程中��
,有24位患者(6.0%)发生了肝脏毒性��
,38位(9.5%)患者出现了视觉症状��
。10位患者因为肝脏毒性作用暂时终止了伏立康唑的服用��
,而有11为患者也因为视觉症状而终止��
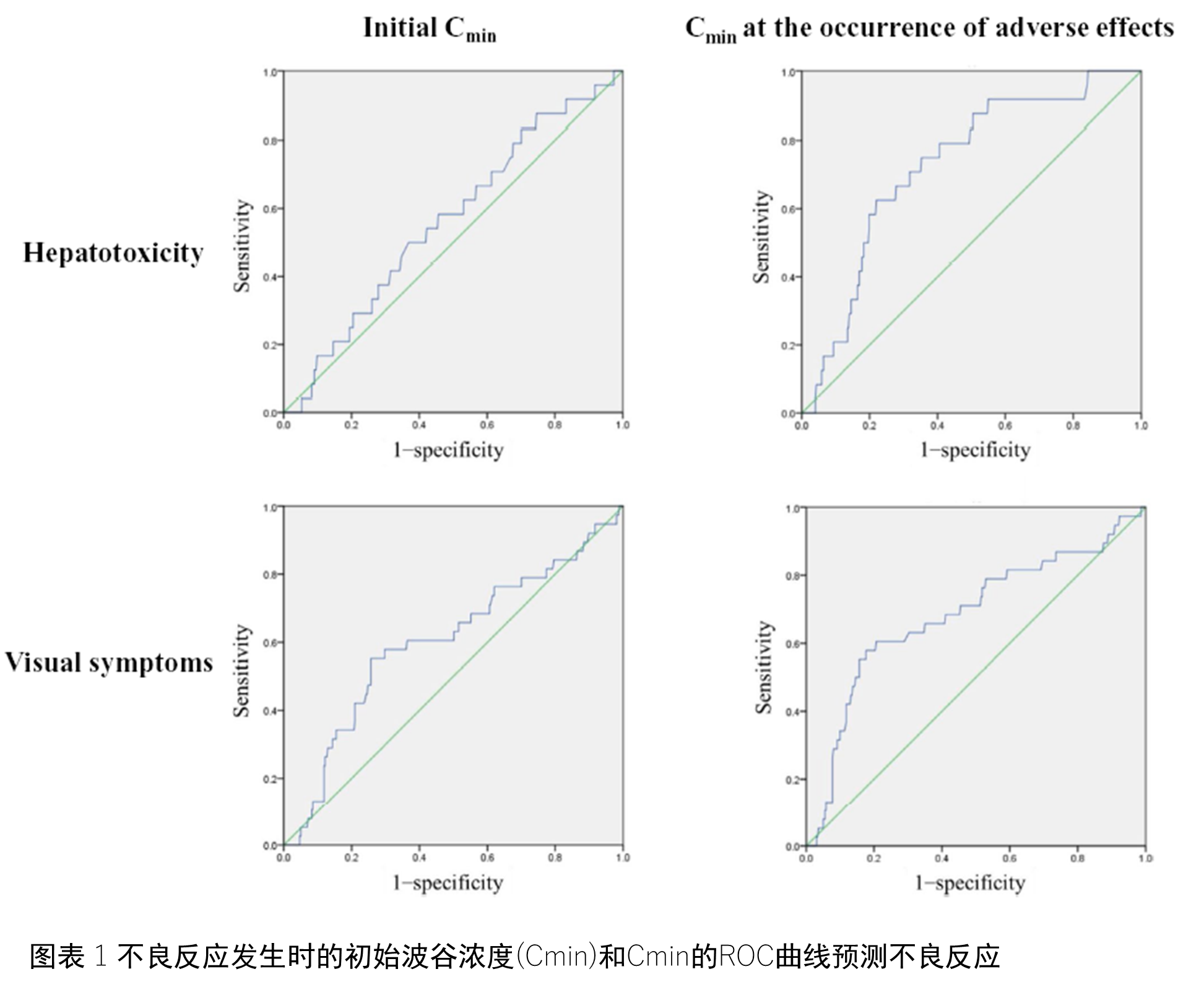
。图1展示了采用ROC曲线分析伏立康唑血药谷浓度和副作用的关系结果��
。尽管较高的起始Cmin与视觉症状有相关性(AUC 0.603, cut-off 4.9μg/mL, OR 3.59, P = .037)��
,但是却与肝脏毒性没有显著相关性(AUC 0.562, cut-off 3.6 μg/mL, OR 1.67, P = .292)��
。但是Cmin却与肝脏毒性(AUC 0.725, OR 5.20, P < .001)和视觉症状(AUC 0.684, OR 5.89, P < .001)都有明显相关性��
。推算的肝脏毒性Cmin cut-offs值为4.2 ug/ml�
, 视觉症状Cmin cut-offs值为3.5ug/ml��
。针对Cmin较高且发生了肝脏毒性(8例)或视觉症状(27例)的患者进行了剂量减量�
,使其Cmin恢复到标准水平�
,其副作用均得到了缓解��,并完成了整个伏立康唑的治疗疗程��
。表格3显示了其实Cmin的分布以及剂量的调整�
。
表格 3 根据伏立康唑初始谷浓度(Cmin)调整伏立康唑剂量
| Subsequent Cmin (ug/mL) |
Dose adjustment | <1 | 1-5 | ≥5 | Total | No data available |
Dose adjustment (n=120) | 3(2.7%) | 96(87.3%) | 11(10.0%) | 110(100%) | 10 |
Dose reduction (n=95) | 1(1.2%) | 74(87.0%) | 10(11.8%) | 85(1009%) | 10 |
Dose increase (n=25) | 2(8.0%) | 22(88.0%) | 1(4.09%) | 25(100%) | 0 |
Same dose (n=220) | 18(11.6%) | 128(82.69%) | 9(5.89%) | 155(100%) | 65 |